d.ecs storage manager NAS
The NAS module allows d.ecs storage manager to store documents on a NAS system (NAS = Network Attached Storage).
Warning
Technically speaking, the NAS module always stores documents / content on an unprotected area which can be manipulated and which is thus not audit-proof.
When using the NAS-variant for the audit-proof storage, then respective measures and protective mechanisms must be implemented to ensure and warrant the completeness, unchangeability and genuine storage on the storage media. These measures and protective mechanisms must be documented in a process manual.
In contrast to the NAS-solution, the other systems supported by d.ecs storage manager ((Centera, Data Domain, NetApp, TSM / Jukebox , Silent Cubes , FileLock , iCAS , HCP) ensures audit compliance from a technical point of view when used correctly..
Configuration
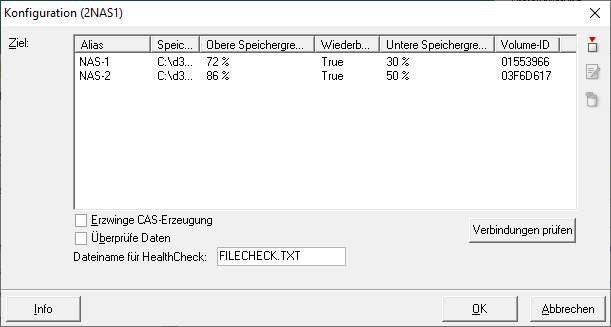 |
Objective: List of the target paths where the documents are stored and their properties.
Alias: Alias name of the volume.
Storage path: Target path where the documents are stored.
Upper storage limit: Specifies how much storage space may be used for storing data.
Rewritable: If this option is set, the data will be re-written as soon as the available storage space falls below the Lower storage limit.
Lower storage limit: Specify the percentage of disk space which may be occupied before documents can be stored again.
Volume ID: Every storage path gets a unique volume ID.
Force CAS creation: If this option is enabled, then the documents are stored in CAS containers. These containers have a unique ID which is used to verify the consistency of a document during restore. During the recovery it is checked, if the data in a CAS container are unchanged. This should only be enabled in connection with ecspand or if the consistency of the data on the NAS should be verifiable.
Validate data: If this option is enabled, a file comparison based on the RipeMD256 mechanism is performed after having copied a file to the NAS-volume. This ensures that the file as completely transferred.
File name for HealthCheck: File name to be used during the system check by the HealthCheck process.
Volume configuration
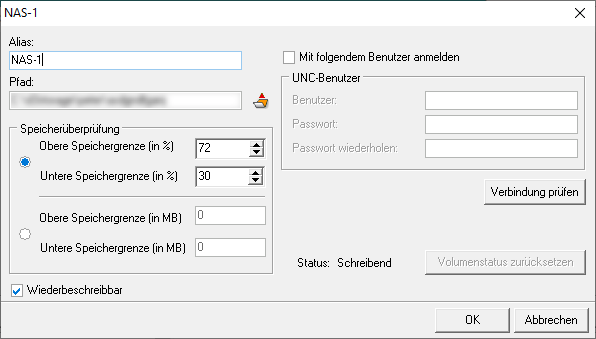 |
Alias: Alias name for the volume. If a name is specified here then this is used instead of the volume ID in the web interface. This is used for a better overview.
Storage path: Specify a path here where the documents are stored
Upper storage limit (in %): Here you can define a percentage of how much storage space may be used for the storage of data.
Lower storage limit (in %): Specify the percentage of hard disk space which may be occupied before documents can be stored again.
Upper storage limit (in MB): Here you can define in MB how much storage space may be used for the storage of data.
Lower storage limit (in MB): Specify the percentage of hard disk space which may be occupied before documents can be stored again.
Rewritable: This option is only available, if more than one volume is configured and specifies, if a volume should be rewritten as soon as the lower storage threshold of the volume is exceeded (e.g. by deleting old documents).
Log in with the following user: If this parameter is enabled, the d.ecs storage manager automatically tries to log in to the respective volume. This parameter only has to be enabled, if the d.ecs storage manager is executed under a user account which does not have access to the volume.
User: User to be used for the login to the volume.
Password/Confirm password: Password of the user to be used for the login to the volume.
Status: One of three possible values of the volume is displayed. Use the Reset volume status button to reset the status of a volume to Waiting.
Waiting: There is currently no writing on the volume.
Writing: Currently writing on the volume.
Full: The volume was written on until it exceeded the configured memory limits. The volume cannot and will no longer be written to.
Index recovery
The d.ecs storage manager NAS module allows to recover the internal document index after a loss.
For this effect, it browses the specified target directory for documents and thus rebuilds the index.
This type of index recovery should only be used, if no index-recovery-files (*.IR) exist to restore the index (also see Tab: Database logging).
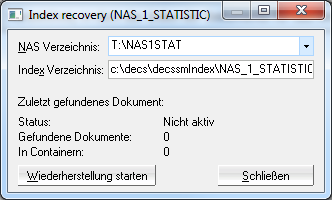 |
NAS directory: Directory on the NAS system to be searched for documents.
Index Directory: Directory where the index of the documents for the NAS system is to be stored.