Basic information about mapping
The mapping feature in DMSApp lets you establish a connection between any third-party application, such as an e-mail application or ERP system, and a d.3 repository. This mapping feature is the basis for creating extensions and functions that make it easier for you to program functions, e.g. saving elements that come from another ERP system.
For example, if you would like to store your e-mails in a d.3 repository by default, it is useful to directly map the item "E-mail" to a d.3 category and the related d.3 properties. You can save your users from manually mapping properties and categories if you define the mapping as an administrator. Thus, your source system is the e-mail application, the destination system is a d.3 repository. By default, any e-mail has specific properties, among them are, for example, the sender and the recipient as well as the subject of an e-mail. You can use these typical properties for an e-mail to map them to a d.3 category and the d.3 properties. This mapping automatically maps the e-mail to the correct category, for example. The typical e-mail properties are then automatically written into d.3 properties.
To use the mapping feature effectively, you can make the data model of a third-party application available as a source to connect it to the data model of the d.3ecm target (DMSApp). The data model description is designated as the source.
For instance, you may want to store your data from an e-mail application (e-mails, attachments) in a d.3 repository and save your users from manually mapping d.3 categories and d.3 properties. In this case, the e-mail application is your source system. The e-mail is a source of this source system, which has certain categories and properties by default. These typical categories and properties for the source must be “translated” into the d.3ecm data model. This method is the only way for you to ensure that the fields are mapped correctly by default when you save the items from the e-mail application.
An e-mail application provides you with a variety of metadata. This may include the sender, recipient and subject line, for example. You can connect this source metadata to the metadata in a d.3 repository, where the items from the source are saved. For example, in a d.3 repository, you can map an e-mail to the document type Correspondence and the subject (source property Mail_Subject) to the d.3 property Subject.
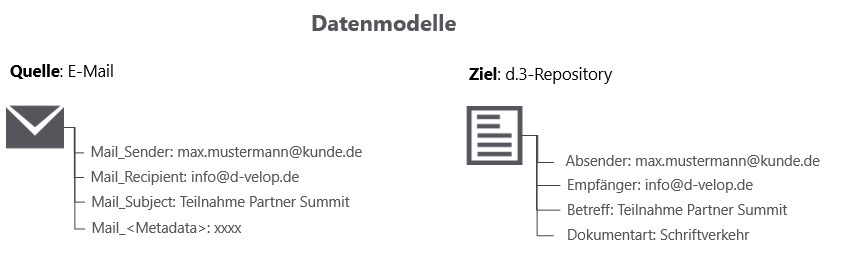
Understanding the relationship between the possible categories and properties of a source and the categories and properties in d.3ecm is important for mapping.